SNMP trap receivers are systems or software components designed to receive and process SNMP traps — which are asynchronous notifications sent from network devices like switches, routers, or servers.
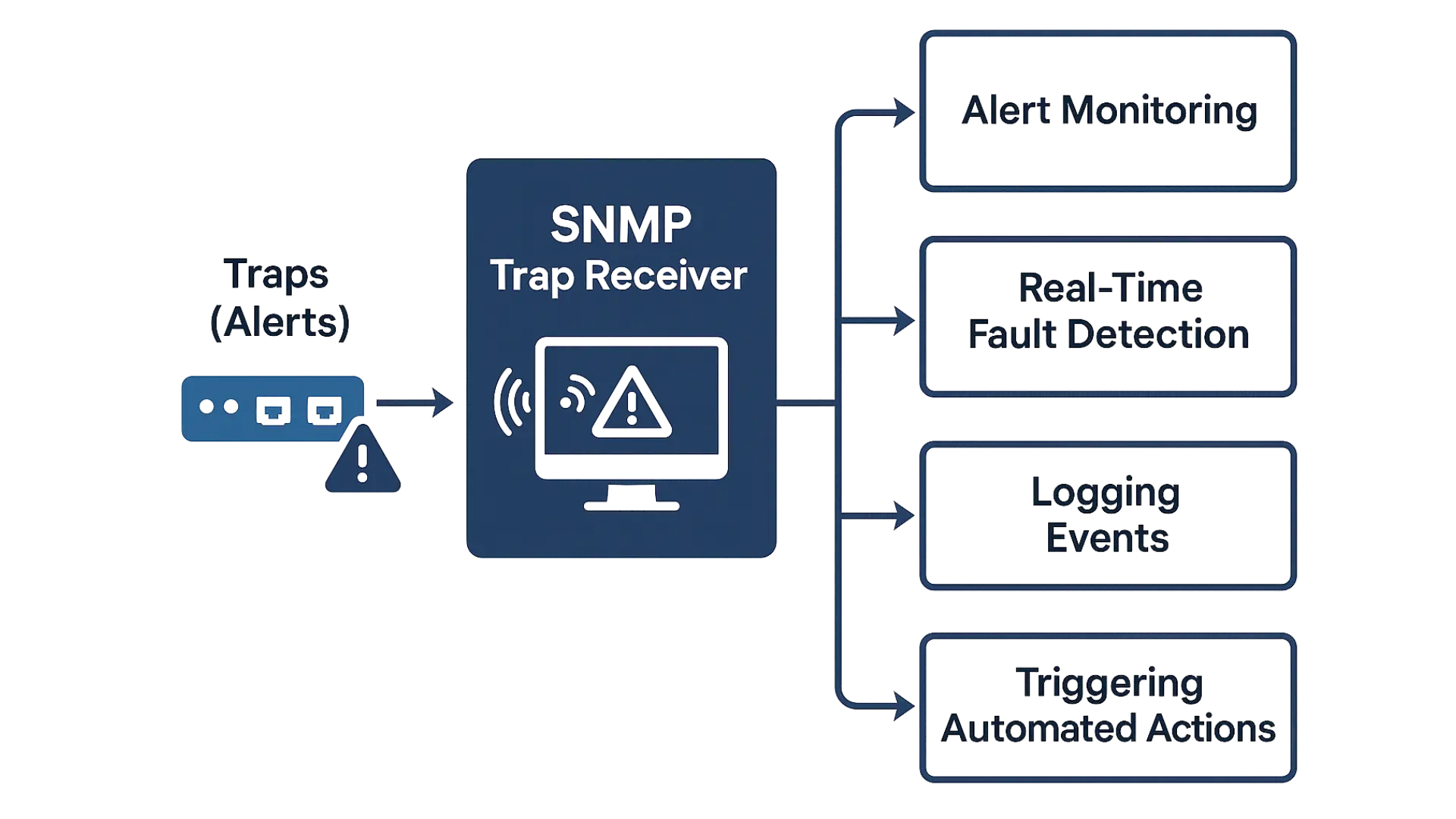
Purpose of SNMP Trap Receivers:
- Alert Monitoring
They receive traps (alerts) when something important happens on a network device — such as link down, CPU overload, temperature warnings, or failed logins. - Real-Time Fault Detection
Since traps are sent immediately when an event occurs, trap receivers help admins respond quickly to network issues. - Logging Events
Trap receivers often log received traps into databases or monitoring systems for analysis, audits, or reporting. - Triggering Automated Actions
Some systems can act on specific traps — for example, sending an email, creating a ticket, or rebooting a service.
Example:
- A router detects that one of its interfaces has gone down.
- It sends an SNMP trap to the trap receiver.
- The trap receiver logs the event and alerts the network admin or monitoring dashboard
Software Required
MapleLink Lite User Interface (Enter the network switch’s IP address into a web browser to access its web interface.
Hardware Required
- MS1-L05G01F
- MS1-L08G
- Embedded Industrial Box PC (A web browser is required. Use one of our Industrial Box PCs.)
What is SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a standard protocol used in network management systems to monitor and manage devices connected to a network. It helps detect conditions that may require administrative attention, such as faults or performance issues. Developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), SNMP is part of the Internet Protocol Suite and includes an application-layer protocol, a standardized data model (schema), and a collection of data objects.
SNMP makes management data available through variables on the devices it monitors. These variables represent aspects of the device’s configuration and status. Network management applications can query these variables to gather information and, in some cases, modify them to update device settings.
SNMP Configuration
Allows the user to enable or disable the SNMP protocol globally. By default, SNMP is disabled. The user can also customize the system name, as well as specify the system location and contact information as needed.
| Node | Command | Description |
| enable | show snmp | This command displays the SNMP configurations |
| configure | snmp (disable/enable) | This command diables/enables the SNMP on the switch. |
| configure | snmp system-name STRING | This command configures a name for the system. (The System Name is same as the host name). |
| configure | snmp system-location STRING | This command configures the location information for the system. |
| configure | snmp system-contact STRING | This command configures contact information for the system |
Example:
– L2SWITCH#configure terminal
– L2SWITCH(config)#snmp enable
– L2SWITCH(config)#snmp system-contact IT engineer
– L2SWITCH(config)#snmp system-location Branch-Office
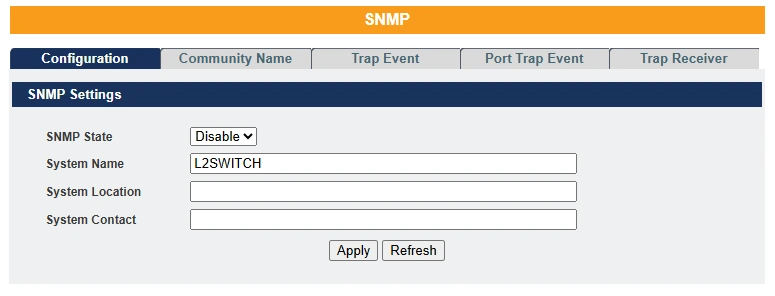
| Parameter | Description |
| SNMP State | Select option to enable / disable the SNMP on the switch |
| System Name | User can configure system name |
| System Location | User can configure the switch deployed location for reference |
| System Contact | User can configure System Contact person information like name or number |
SNMP Community Name
An SNMP Community Name is basically like a password or key that allows access to a network device’s management information using SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). It’s used mainly in SNMP v1 and v2c, which don’t have strong authentication.
Here’s the breakdown:
- Purpose: It controls who can read or modify information on a device like a router, switch, or server.
- Types:
- Read-only community (commonly
public) – allows viewing device information but not changing it. - Read-write community (commonly
private) – allows viewing and modifying settings.
- Read-only community (commonly
- Usage: When an SNMP manager queries a device, it includes the community name. If the device recognizes it, it responds; if not, access is denied.
Think of it like a door key: the right key lets you in (read or write), the wrong key leaves you outside.
SNMP Community Strings:
In SNMP v1 and SNMP v2c environments, community strings function like passwords and are used to define the security parameters for SNMP clients. By default, the SNMP community string is set to “public” for both versions.
Network ID of Trusted Host:
The IP address consists of two parts: the Network ID and the Host ID, where:
- Network ID = (Host IP & Subnet Mask)
When configuring a trusted host, users should enter only the Network ID, leaving the Host ID as 0.
– For example, if a user enters the full IP address 192.168.1.102, the system will automatically reset the Host ID, resulting in 192.168.1.0.
Configuration
| Node | Command | Description |
| configure | snmp community STRING (ro/rw) trusted-host IPADDR/Subnet Mask | This command configures the SNMP community name, Permissions (ro/rw), Trusted host IP/Subnet mask. |
Example:
– L2SWITCH#configure terminal
– L2SWITCH(config)#snmp community public rw trusted-host 192.168.200.106/24
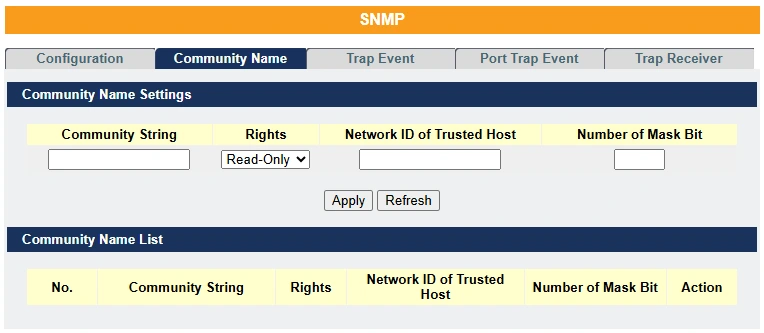
| Parameter | Description |
| Community String | Enter a Community string; this will act as a password for requests from the management station. An SNMP community string is a text string that acts as a password. It is used to authenticate messages that are sent between the management station (the SNMP manager) and the device (the SNMP agent). The community string is included in every packet that is transmitted between the SNMP manager and the SNMP agent. |
| Rights | Select Read-Only to allow the SNMP manager to use this string to collect information from the Switch. Select Read-Write to allow the SNMP manager to use this string to create or edit MIBs (configure settings on the Switch). |
| Network ID of Trusted Host | Type the IP address of the remote SNMP management station in dotted decimal notation, for example 192.168.1.0. |
| Number of Mask Bit | Type the length of the subnet mask bits. |
| Apply | Click Apply to for settings to take effect. |
| Refresh | Click Refresh to begin configuring this screen afresh. |
| No. | This field displays the index number of an entry. |
| Community String | This field displays the community string of an entry. |
| Rights | This field displays the right of an entry. |
| Network ID of Trusted Host | This field displays the network ID of trusted host of an entry. |
| Number of Mask Bit | This field displays the length of the subnet mask bits of an entry. |
| Action | Click the Delete button to remove the entry. |
SNMP Trap Event Settings
The features allow users to enable/disables individual trap notifications.
| Node | Command | Description |
| enable | show snmp trap-event | This command displays the SNMP configurations. |
| configure | snmp trap-event alarmover- heat (disable/enable) | This command enables/disables the alarmover- heat trap. |
| configure | snmp trap-event alarmover- load (disable/enable) | This command enables/disables the alarmover- load trap. |
| configure | snmp trap-event alarmpower- fail (enable/enable) | This command enables/disables the alarmpower- fail trap. |
| configure | snmp trap-event bpdu (disable/enable) | This command enables/disables the BPDU port state change/BPDU Root Guard/BPDU Guard trap |
| configure | snmp trap-event loop-detection (disable/enable) | This command enables/disables the loopdetection trap. |
| configure | snmp trap-event portadmin- state-change (disable/enable) | This command enables/disables the portadmin- state-change trap. |
| configure | snmp trap-event portlink- change (disable/enable) | This command enables/disables the port-linkchange trap. |
| configure | snmp trap-event powersource- change (disable/enable) | This command enables/disables the powersource- change trap. |
| configure | snmp trap-event stptopology- change (disable/enable) | This command enables/disables the stptopology- change trap. |
| configure | snmp trap-event trafficmonitor (disable/enable) | This command enables/disables the trafficmonitor trap. |
Configuration
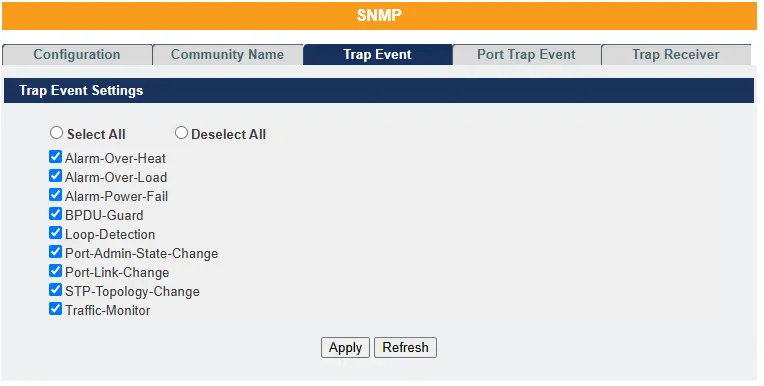
The features allow users to enable/disables individual trap notification.
| Alarm-Over-Heat Alarm-Over-Load Alarm-Power-Fail | – Trap when the system’s temperature is too high. – Trap when system is overloaded. – Trap when system power is over voltage/under – voltage/RPS over voltage/RPS under voltage. |
| BPDU-Guard Loop-Detection | – Trap when port is blocked by BPDU Guard/BDPU Root Guard/BPDU port state changed. – Trap when port is blocked by Loop Detection |
| Port-Admin-State-Change Port-Link-Change STP-Topology-Change Traffic-Monitor | – Trap when port is enabled/disable by administrator. – Trap when port linking up/down is changed. – Trap when the STP topology changes. – Trap when port is blocked by Traffic Monitor. |
| Parameter | Description |
| Select all | Enables all trap events. |
| Deselect All | Disables all trap events. |
| Apply | Click Apply to configure the settings. |
| Refresh | Click Refresh to begin configuring this screen afresh. |
SNMP Port Link-Change Trap Settings
The features allow users to enable/disables port-link-change trap notification by individual port.
Configuration:
| Node | Command | Description |
| enable | show snmp port-link-change-trap | This command displays the SNMP port link-change trap configurations. |
| interface | snmp port-link-change-trap | This command enables the link change trap on the specific port. |
| interface | no snmp port-link-change-trap | This command disables the link change trap on the specific port. |
| config | interface range (fastethernet1/0/ | gigabitethernet1/0/) PORTLISTS | This command enters the interface configure node. |
| if-range | snmp port-link-change-trap | This command enables the link change trap on the specific ports. |
| if-range | no snmp port-link-change-trap | This command disables the link change trap on the specific ports. |
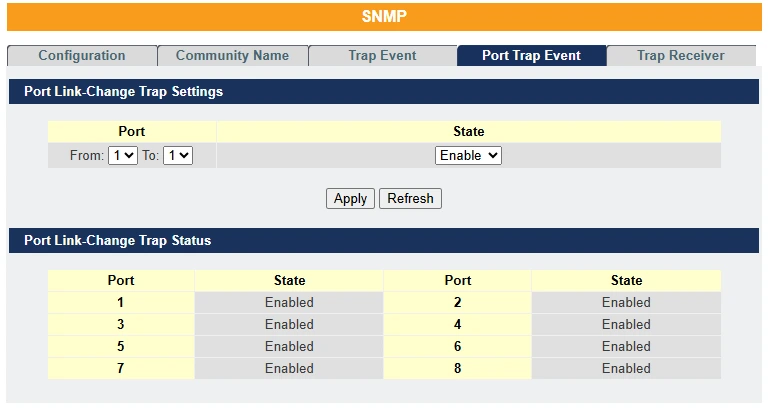
| Parameter | Description |
| Port | Selects the range of ports. |
| State | User can enable /disable trap events when port link change. |
| Apply | Click Apply to configure the settings. |
| Refresh | Click Refresh to begin configuring this screen afresh. |
SNMP Trap Receiver Settings
SNMP Trap Receiver Configuration
| Node | Command | Description |
| configure | snmp trap-receiver IPADDR VERSION COMMUNITY String | This command configures the trap receiver’s configurations, including the IP address, version (v1 or v2c) and community String. |
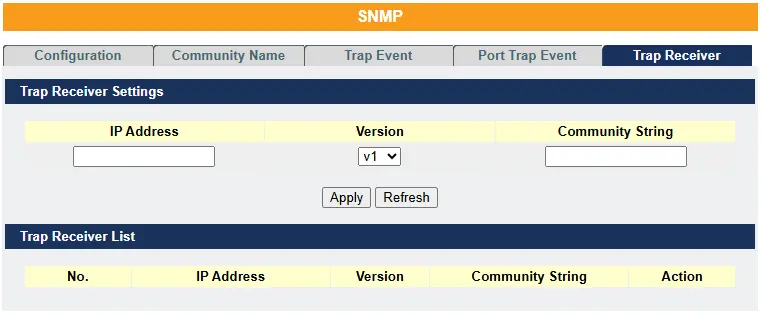
| Parameter | Description |
| IP Address | Enter the IP address of the remote trap station in dotted decimal notation. |
| Version | Select the version of the Simple Network Management Protocol to use. v1or v2c. |
| Community String | Specify the community string used with this remote trap station. |
| Apply | Click Apply to configure the settings. |
| Refresh | Click Refresh to begin configuring this screen afresh. |
| Trap Receiver List | |
| No. | This field displays the index number of the trap receiver entry. Click the number to modify the entry. |
| IP Address | This field displays the IP address of the remote trap station. |
| Version | This field displays the version of Simple Network Management Protocol in use. v1or v2c. |
| Community String | This field displays the community string used with this remote trap station. |
| Action | Click Delete to remove a configured trap receiver station. |
Real-Life Scenario
Scenario: Automated Manufacturing Plant — CNC Machine Network Monitoring.
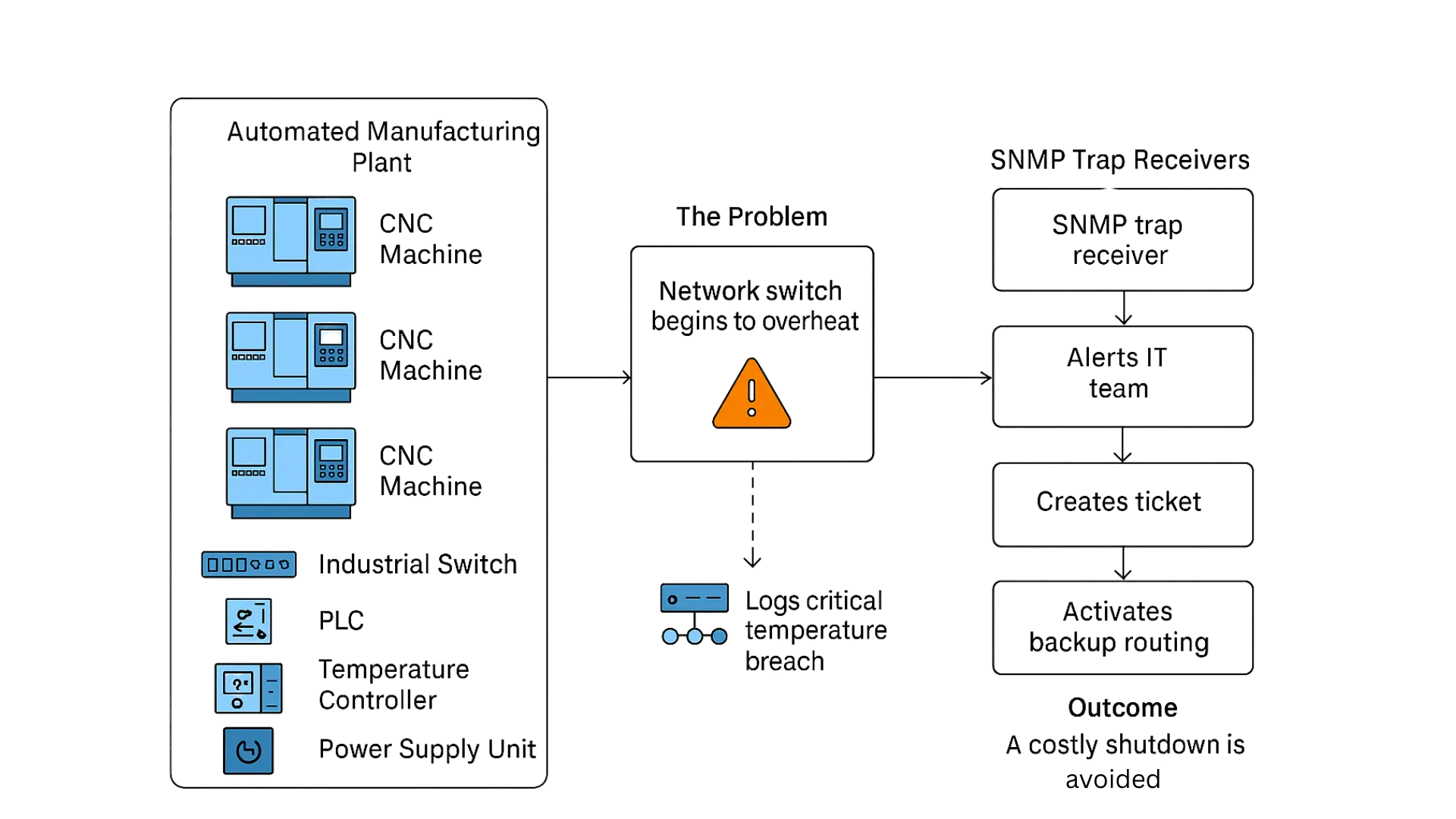
Setting:
An automated manufacturing facility uses a fleet of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines controlled and monitored through a centralized network. Each CNC machine, along with supporting devices like industrial switches, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), temperature controllers, and power supply units, is SNMP-enabled.
The Problem:
One day, a network switch connecting several CNC machines begins to overheat due to a failing internal fan. If it fails completely, it will halt production in that section of the plant.
The Role of SNMP Trap Receivers:
- The network switch detects the high internal temperature and sends an SNMP trap to the plant’s SNMP trap receiver system.
- The SNMP trap receiver logs the event and recognizes it as a critical temperature threshold breach.
- Within milliseconds, it:
- Alerts the plant’s IT team via SMS and email.
- Creates a ticket in the facility’s maintenance ticketing system.
- Automatically activates backup routing, rerouting network traffic to maintain uptime while technicians investigate.
- Logs the event in the central monitoring dashboard for auditing.
Outcome:
Thanks to the SNMP trap receiver:
- A costly shutdown is avoided.
- The maintenance crew is dispatched in time to replace the failing fan before complete hardware failure.
- The incident is logged for regulatory and insurance compliance.
Resources & Documentation
Lite-Managed Network Switches Resources:
- Industrial Network Switches
- Industrial Lite-Managed Network Switches – MS1 Series Datasheet
- MS1-L05G01F Quick Start Guide
- MS1-L08G Quick Start Guide
- What is a network switch?
- Industrial Network Switch Operations Manual – Lite-Managed Series
More
Tutorials
Sample Projects
Software Downloads
See our Support Center for a complete list of Quick Start and Installation Guides
About the Author
Trusted source for industrial automation & control solutions
Follow Maple Systems:
