In industrial automation systems, remote I/O is commonly used to connect sensors and actuators that are physically distributed away from the main control panel. By integrating Maple Systems remote I/O directly with a Maple Systems HMI, the HMI communicates with the I/O modules over Ethernet and performs supervisory-level control without requiring a separate PLC.
Centralized HMI Control Over Distributed I/O
As a result, operators can monitor real-time input and output status, command field devices, and supervise machine operation from a single, centralized HMI platform, while the remote I/O serves as the distributed interface for field-level signals.

For example, in a small manufacturing cell, an operator panel is mounted on the front of a machine, while, at the same time, sensors and actuators are distributed along a conveyor and packaging station several feet away. A Maple Systems HMI is mounted directly on the machine and connected to the control network via Ethernet. As a result, the HMI provides a centralized operator interface for monitoring remote I/O signals and commanding field devices located throughout the cell.

Typical Remote I/O Input Devices
- photoelectric and proximity sensors for part detection.
- limit switches for position and guard status.
- operator pushbuttons or pressure switches for machine feedback.
These input signals are read by the HMI to display machine status, generate alarms, and enforce permissive conditions.
At the same stations, the actuating and indicating devices are wired to remote I/O output channels.
Typical output devices could include:
- solenoid valves for pneumatic or hydraulic motion.
- stack lights and indicator lights for machine status.
- relay or contactor coils for enabling motors or control circuits.
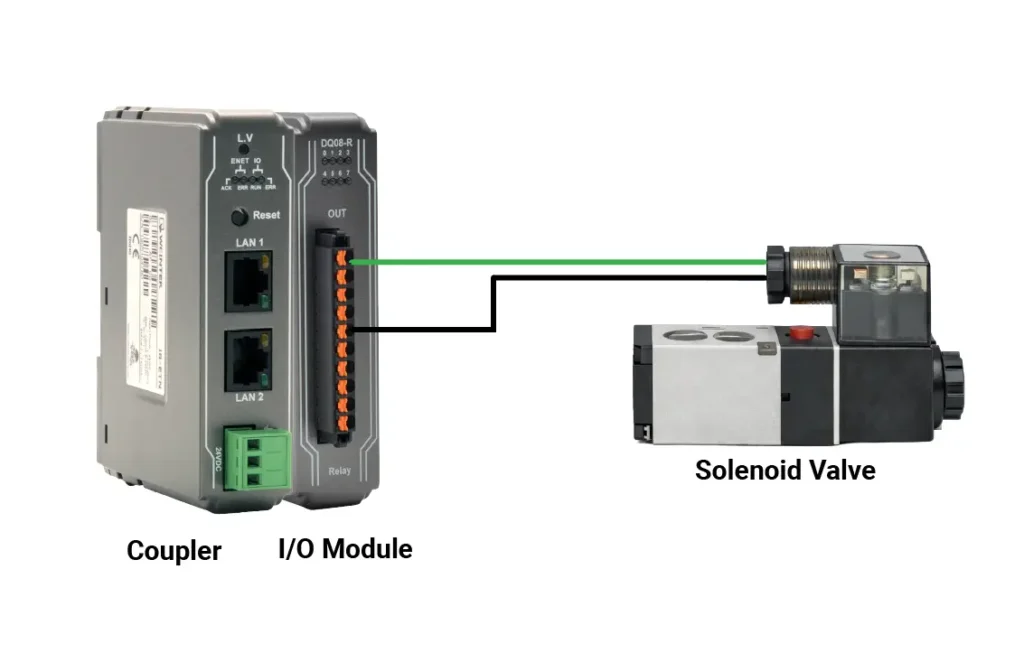

These outputs are driven directly by the HMI to command actuators and visual indicators based on operator actions and input conditions.
Using supported industrial communication protocols such as Modbus TCP or EtherNet/IP (via a Maple Systems adaptor), the HMI establishes direct communication with the remote I/O modules. In this way, the HMI exchanges I/O data directly with the remote I/O hardware and, as a result, eliminates the need for an intermediate PLC for basic monitoring and control functions. Operators can view real-time input and output status, toggle digital outputs, and acknowledge faults directly from the HMI screen. Overall, this approach leads to reduced panel wiring, lower system complexity, faster commissioning, and, ultimately, simplified troubleshooting through clear visibility into field-level I/O.
What You Will Learn
In this tutorial, you will learn the essential steps for integrating Maple Systems remote I/O with a Maple Systems HMI using Modbus TCP in a PLC-less architecture. Specifically, the tutorial covers Ethernet communication setup, device addressing, and key configuration requirements needed to ensure reliable operation. Finally, a simple digital output example is used to demonstrate how to turn a bit on and off directly from the HMI.
Software Required
Hardware Required
- Any Maple Systems HMI can be used. (cMT3218XP used in this example)
- Any Maple Systems Remote I/O Coupler can be used. (iR-ETN used in this example)
- Any Maple Systems Remote I/O Module can be used. (DQ08-R used in this example)
Remote I/O Network Configuration
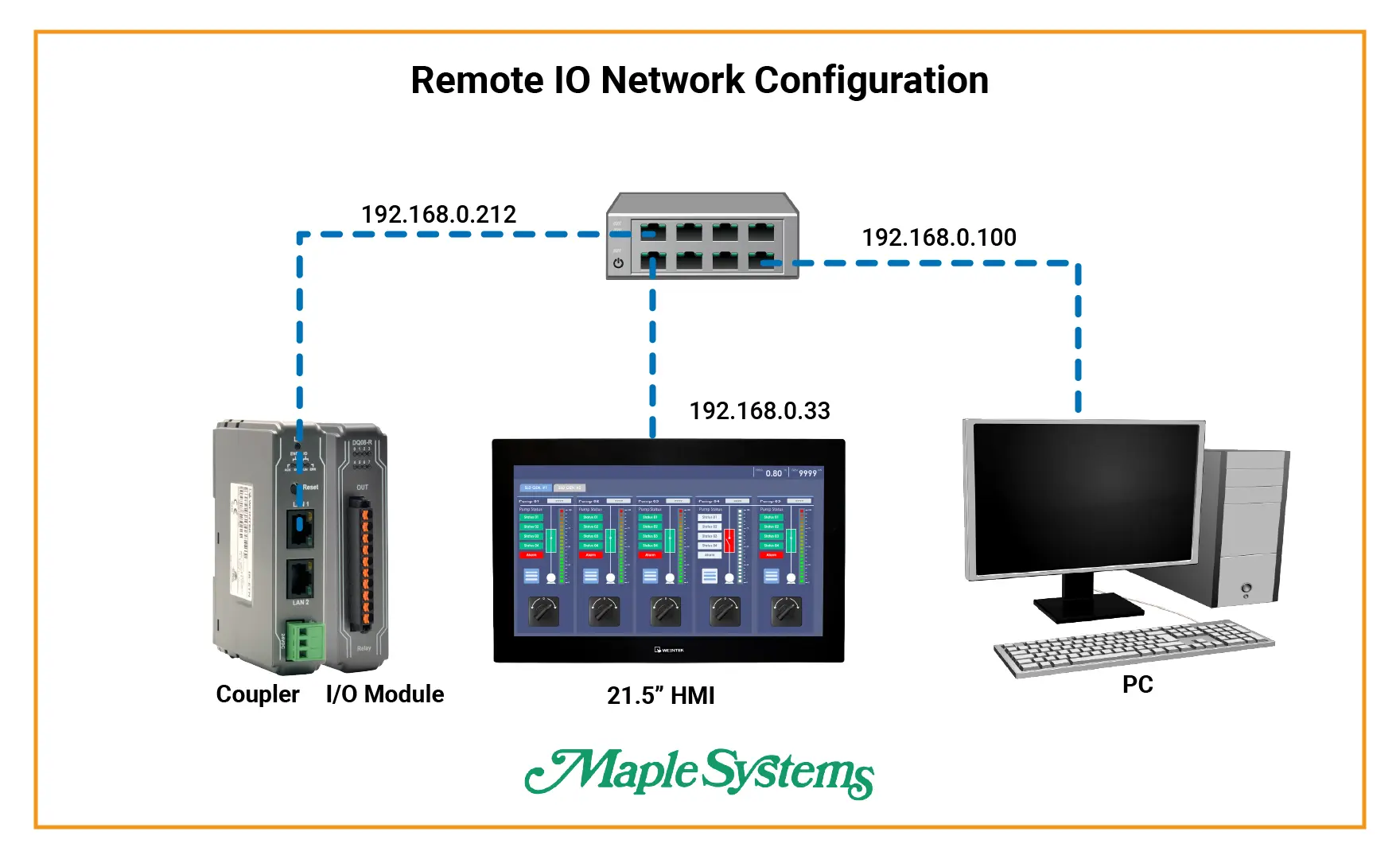
All devices must be configured on the same Ethernet subnet to enable communication between the HMI and remote I/O. Proper subnet configuration is critical for Modbus TCP operation. In this example, the subnet mask is configured accordingly to allow smooth network communication.
Remote I/O Configuration
Follow the steps below to set up your coupler and I/O using EasyRemote I/O.
EasyRemote IO Setup
After downloading and installing EasyRemote I/O, open the software on your PC to begin configuring your Maple Systems remote I/O.
- Click the Add Network Coupler button in the toolbar.
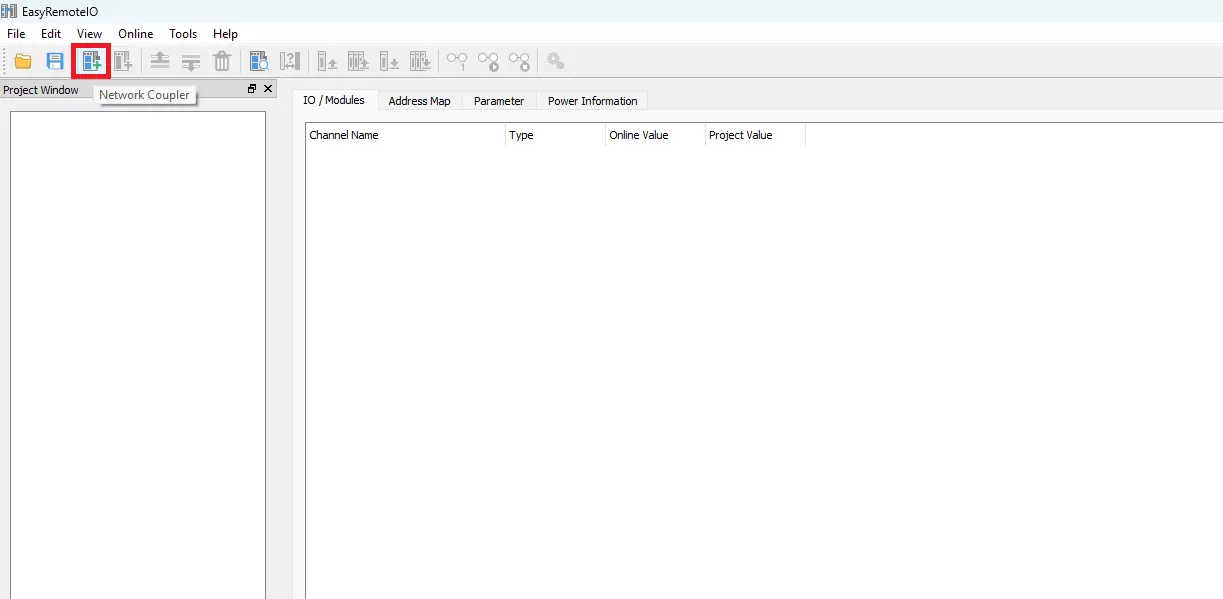
- Select the appropriate remote I/O coupler. In this example, the iR-ETN Ethernet coupler is used.
- Enter the coupler’s IP address. For this setup, the IP address is 192.168.255.15.
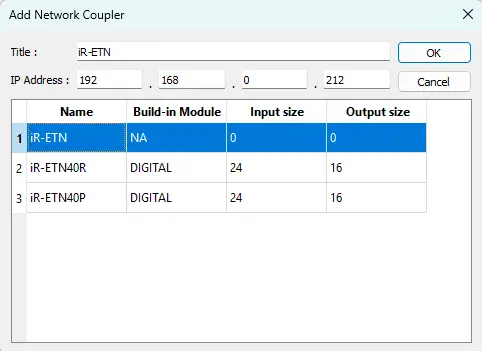
- Once entered, the network coupler is added to the EasyRemote I/O project.
- Click the Add Module button in the toolbar.
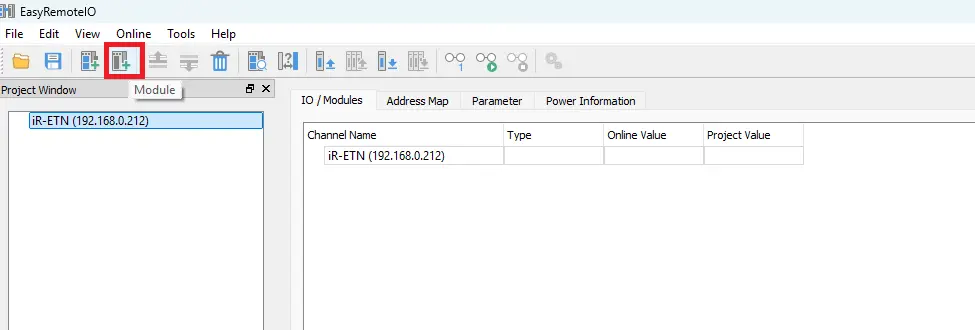
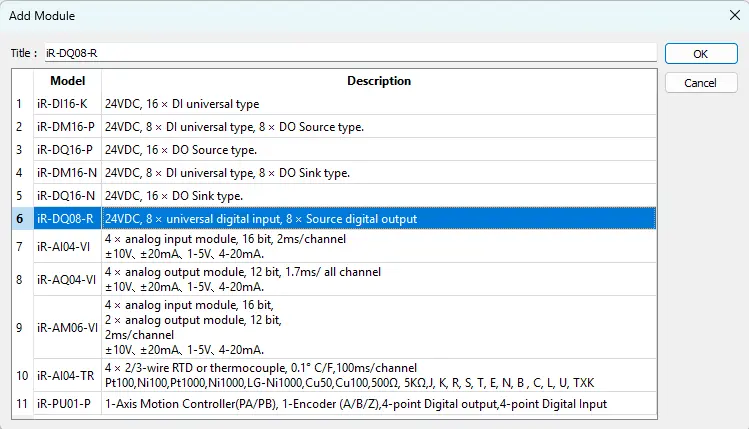
- Select the I/O module type. In this example, a DQ08-R digital output module is used.
- The digital I/O module is now added to the project and ready for configuration.
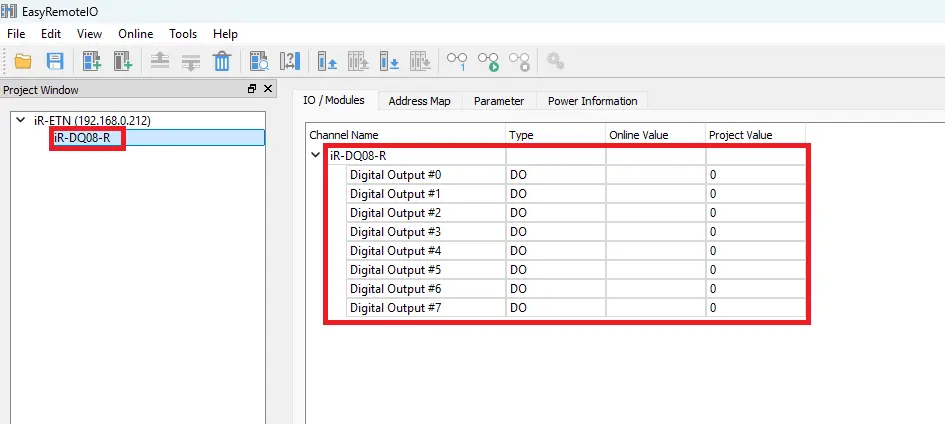
- Now let’s configure the HMI project in EBPro.
HMI Configuration
Now we will set up the HMI using the EBPro software and communicate with the remote I/O using Modbus communication.
EBPro Setup
After downloading and installing EBPro, open the software on your PC to begin setting up your Maple Systems HMI project.
1. Create a New Project
- Start by adding a new project in EBPro.
- For this example, select the cMT3218XP HMI model.
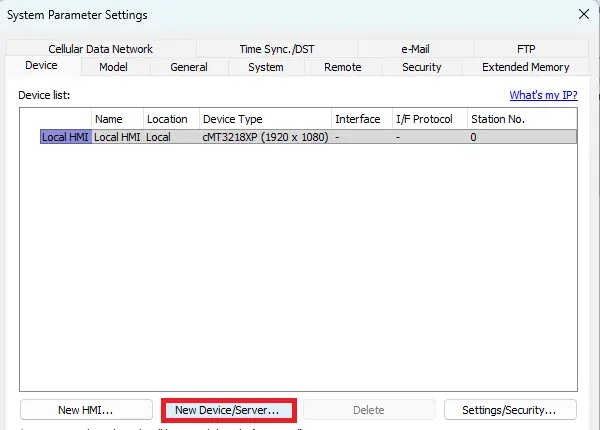
2. Add the Remote I/O Device
- Click New Device/Server.
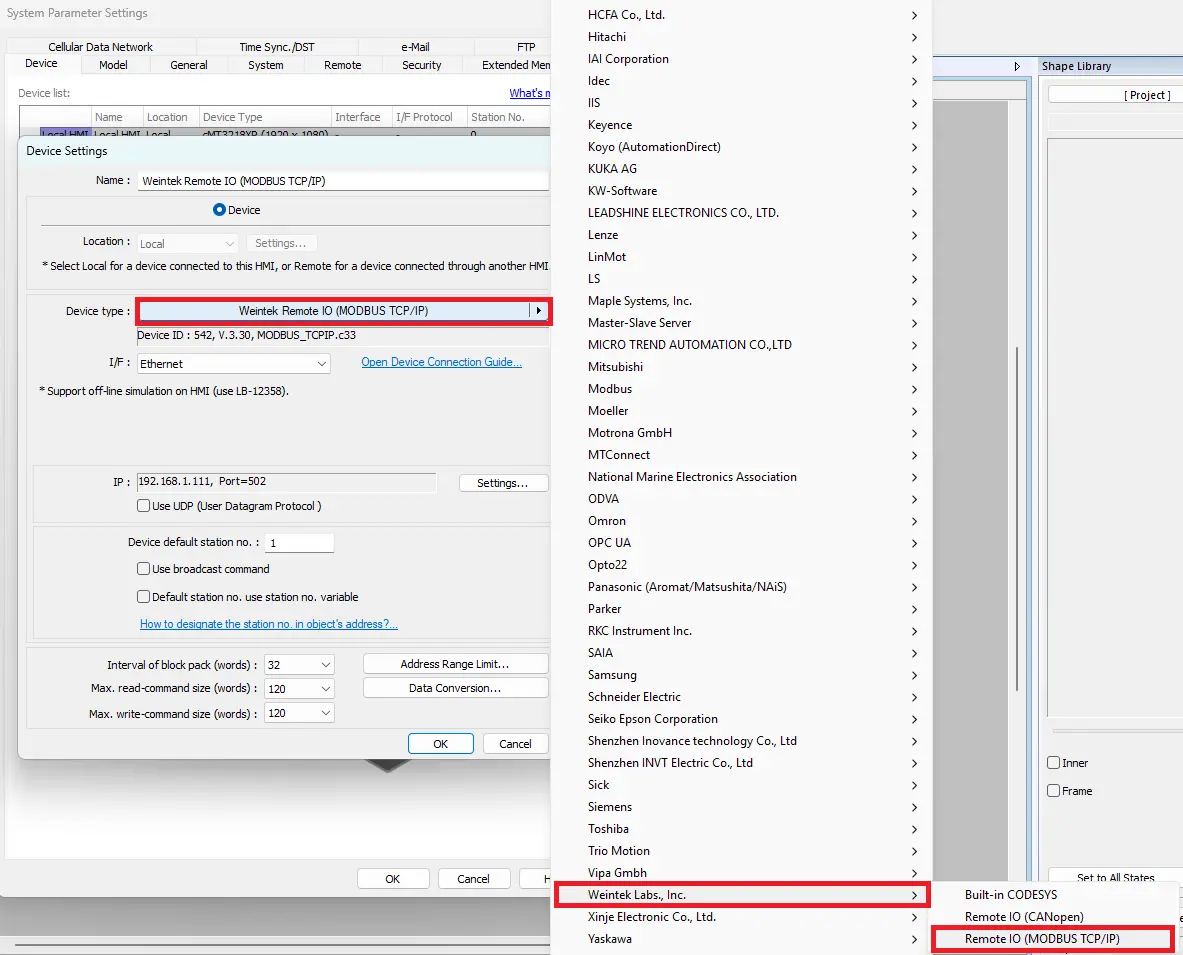
- Select Remote I/O (Modbus TCP/IP) as the device type.
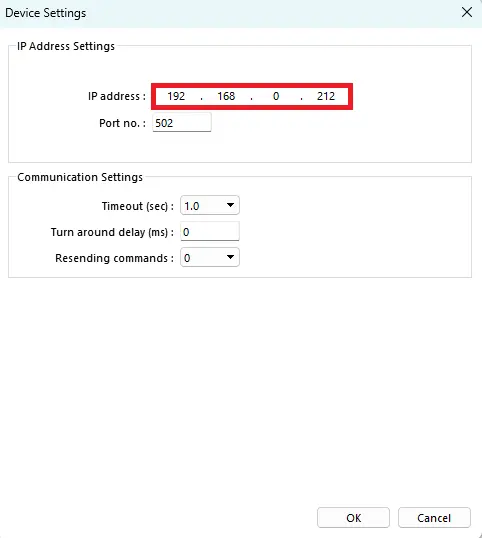
- Open the device Settings
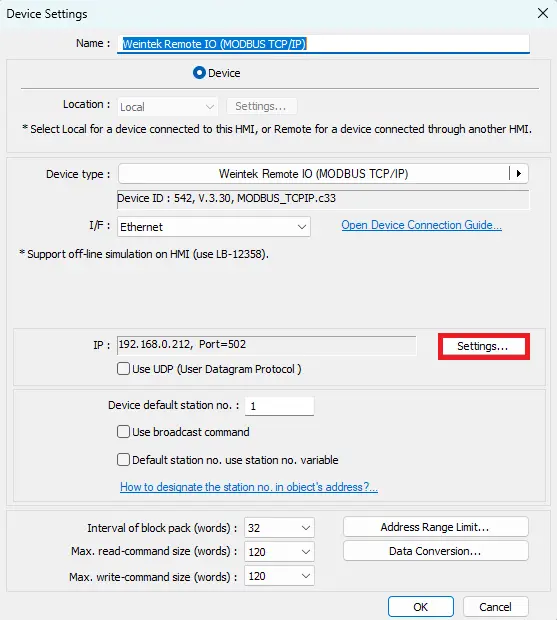
- Ensure the IP address matches the Remote I/O module’s IP.
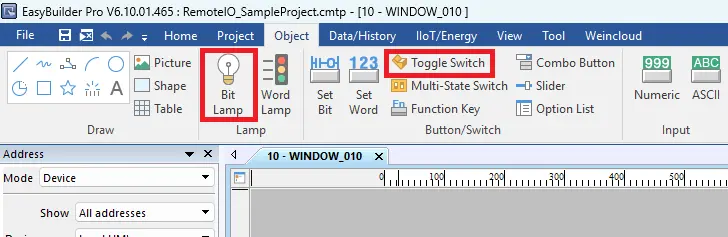
3. Add HMI Objects
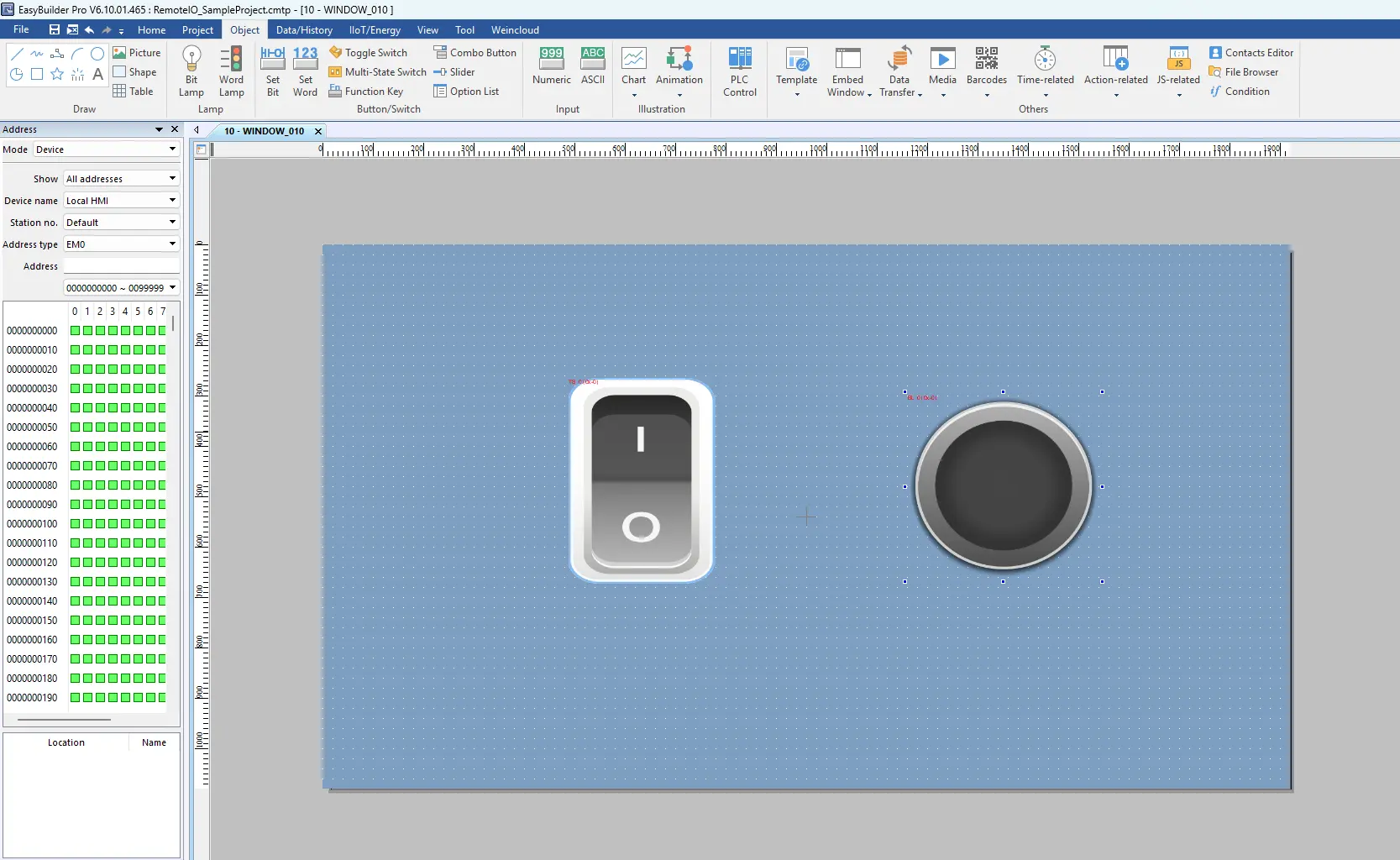
- Add a bit lamp and a toggle switch to the project window.
- Place them where desired in your HMI project layout.
Next we will set up the Modbus TCP communication between the HMI and Remote I/O devices.
Modbus Ethernet Communication
Now we will need to configure the modbus addressing in EasyRemote IO and EBPro.
Modbus Addressing
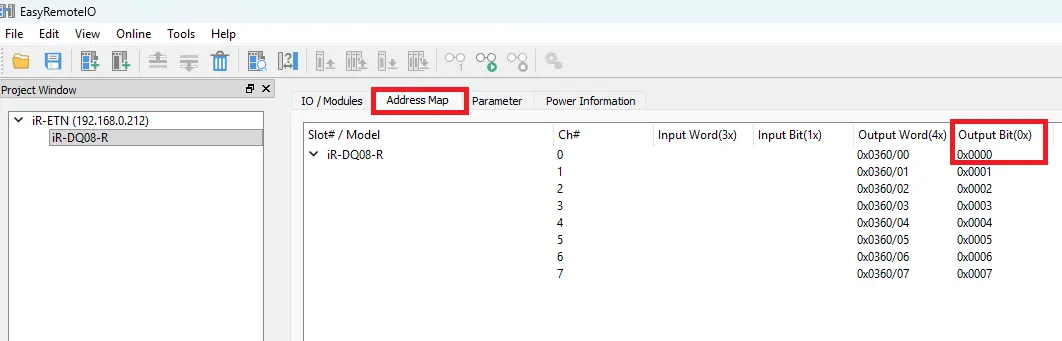
Back in EasyRemote I/O, the next step is to review the address map, which is essential for communicating with your Maple Systems HMI via Modbus TCP. In this example, we will toggle a digital output on and off in EBPro and observe the results in EasyRemote I/O.
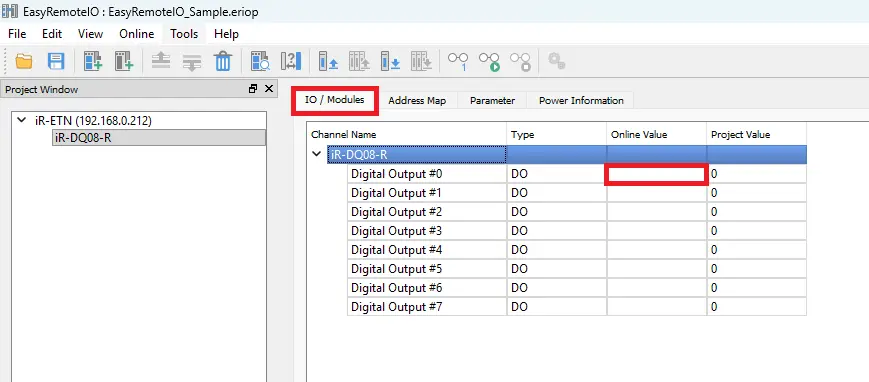
1. Select the Channel
- Use the first channel, Ch# 0, on the iR-DQ08-R digital output module.
- Note the Modbus address for this channel (e.g., 0x).
2. Monitor the Digital Output in EasyRemote I/O
- Navigate to the I/O / Modules tab.
- The channel value will display 0 when off and 1 when on, providing real-time feedback of the digital output state.
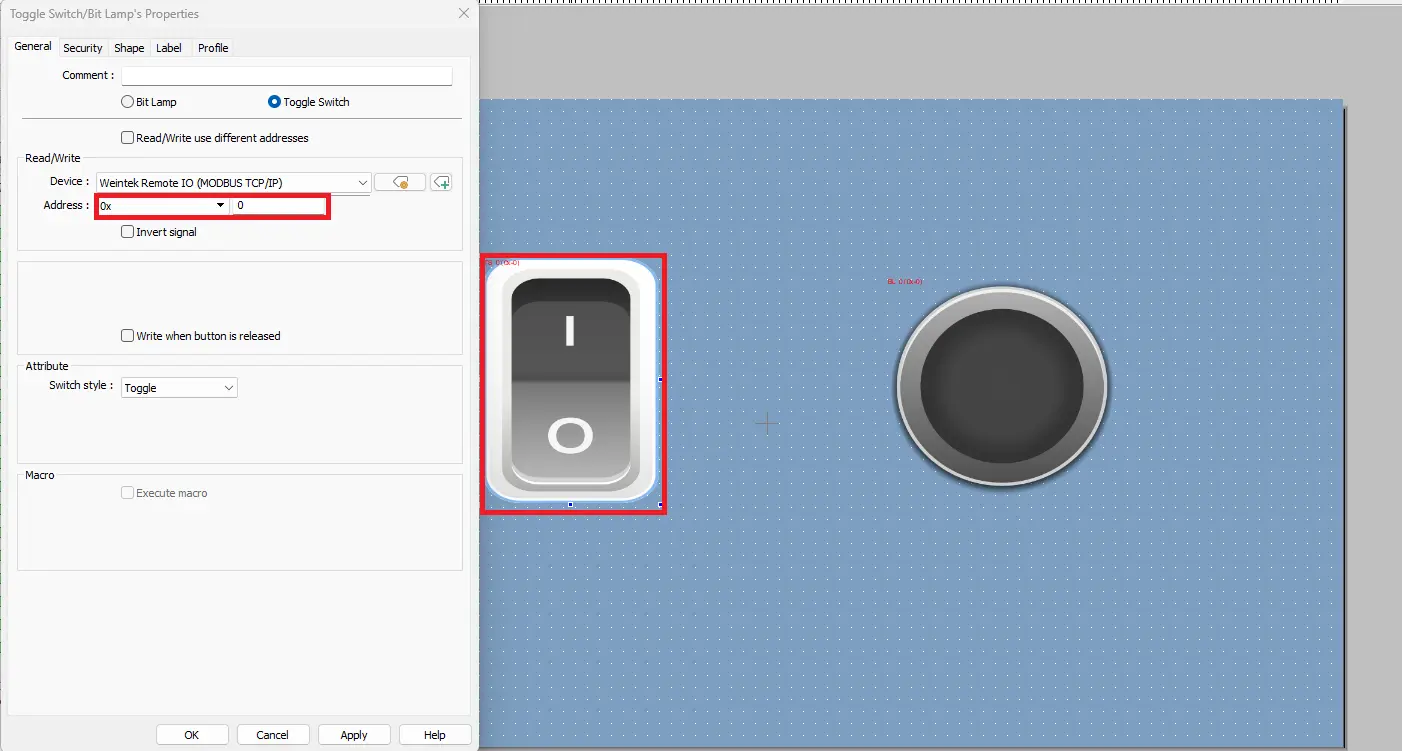
3. Configure Modbus Addressing in EBPro
- In your EBPro project, double-click the toggle switch object.
- Assign it to the Remote I/O device and set the Modbus address to 0x_0 to match Ch# 0 on the iR-DQ08-R.
- Assign the same Modbus address to the bit lamp object to ensure synchronized control and feedback.
Downloading the Project and Going Online
Once configuration is complete, the project is downloaded and brought online in both EasyRemote I/O and EBPro to verify communication.
Downloading and Online Communication
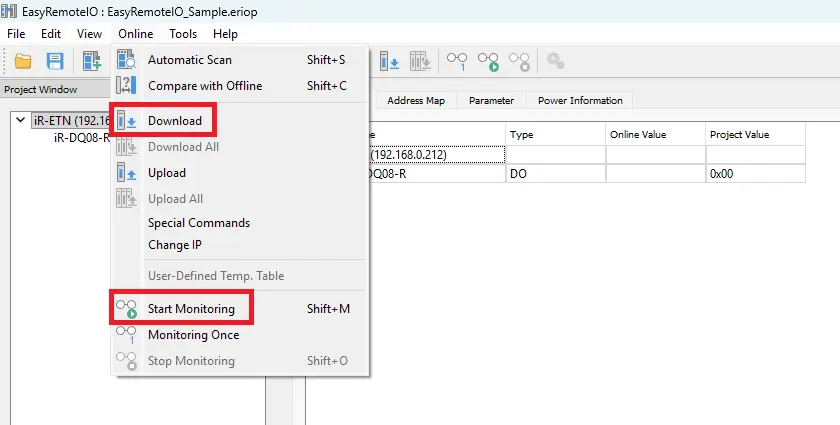
1. Download and Monitor the Project in EasyRemote I/O
- Navigate to Online > Start Monitoring to view live I/O values.
- If you made changes, select Online > Download first to update the project.
- Alternatively, use the Start Monitoring icon or Download icon on the toolbar.
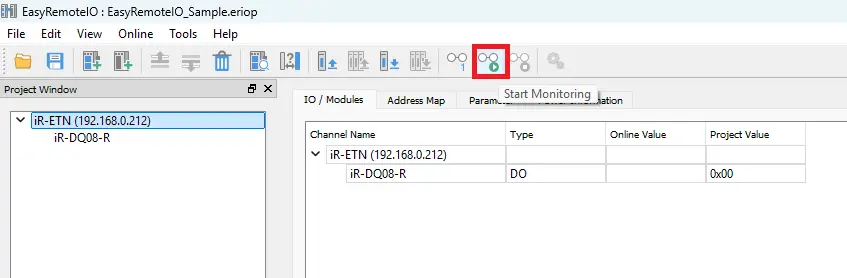
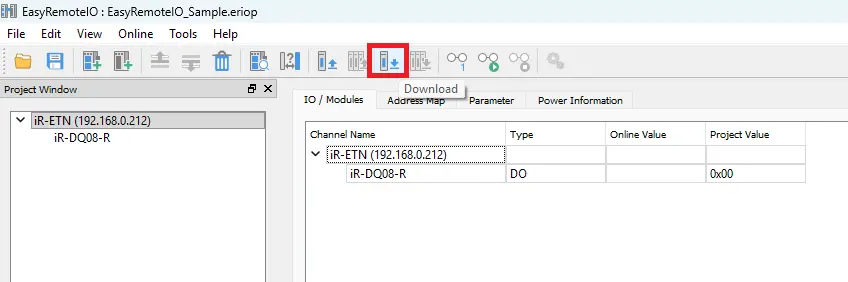
- Click Start Monitoring.
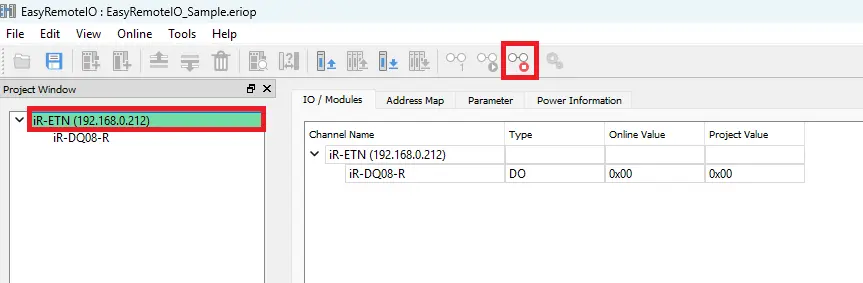
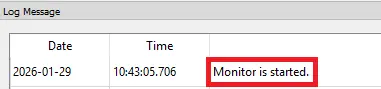
- Check the message window to confirm you are online.
- Open the I/O / Modules tab to see live digital input and output values.

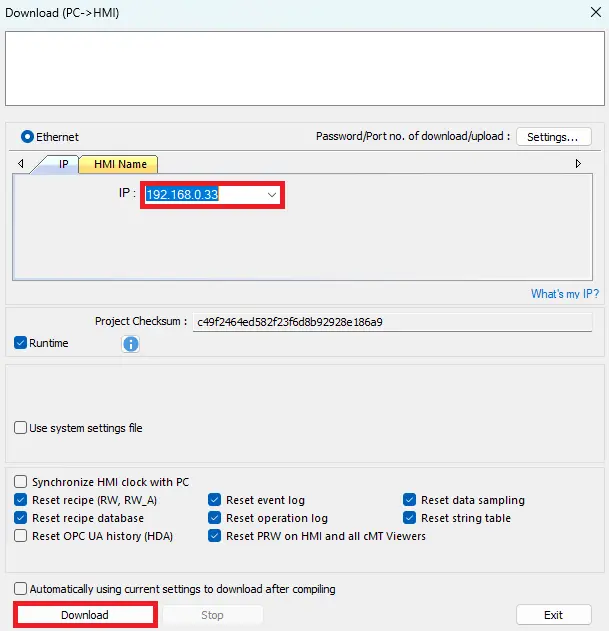
2. Download and Monitor the Project in EBPro
- In EBPro, click the Download icon on the toolbar to open the download window.
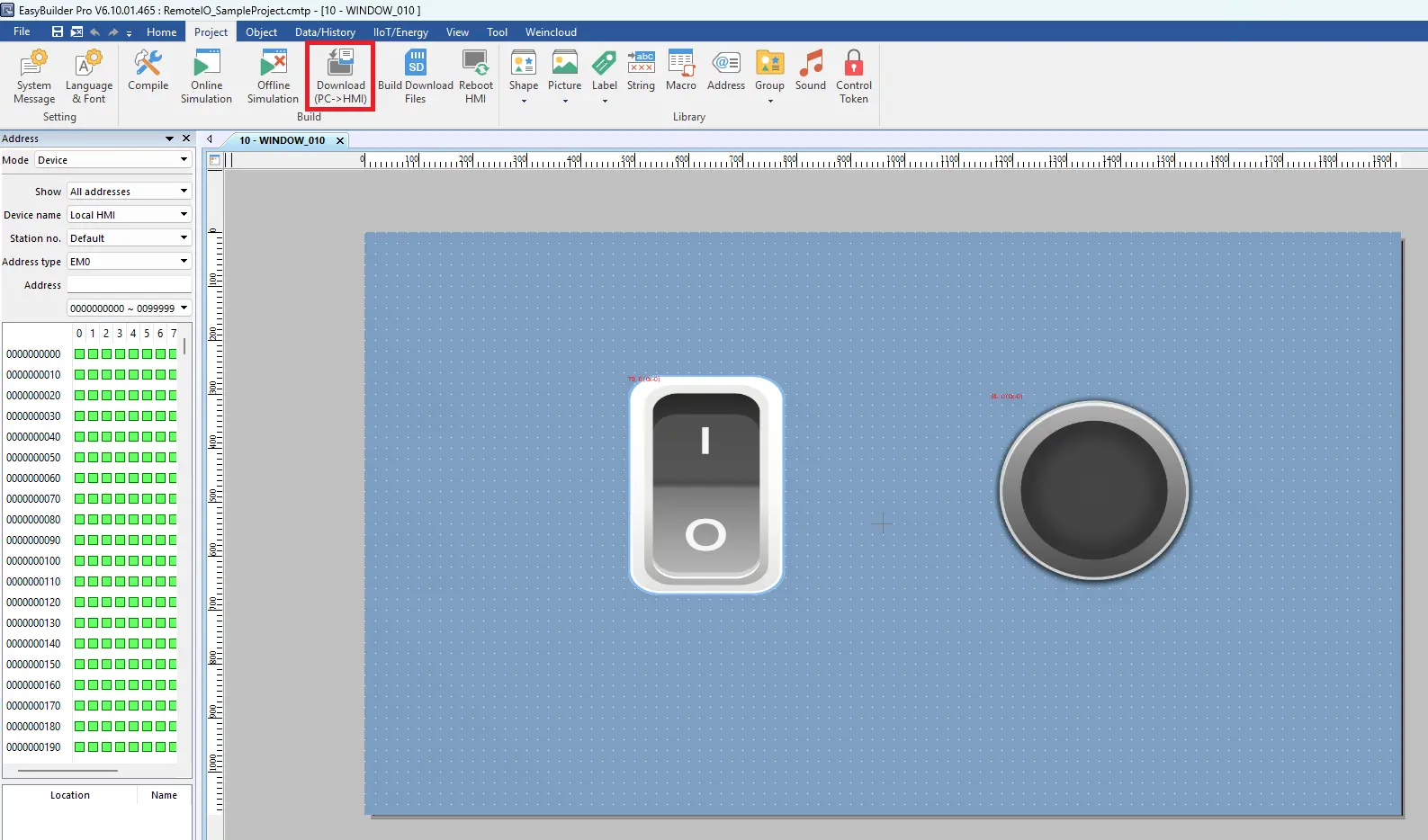
- Verify that the IP address matches the HMI’s IP address.
- Click Download to send the project to the HMI.
Open cMT Viewer on your PC or view the project directly on the HMI.

Live Simulation
You are now online in EBPro and EasyRemote I/O, viewing a live feed from the physical remote coupler and I/O module.
During live operation, the digital output (CH0) can be toggled from the HMI or cMT Viewer, changing values from 0 to 1 in EasyRemote I/O and EBPro. The corresponding LED on the physical remote I/O module confirms real-time output control and successful Modbus TCP communication.
Recap
In this tutorial, we learned how to integrate Maple Systems remote I/O with a Maple Systems HMI using Modbus TCP communication. We walked through configuring the Ethernet network, setting up remote I/O hardware with EasyRemote I/O, and programming HMI communication in EBPro for reliable data exchange.
We also learned how to control and monitor digital outputs from the Maple Systems HMI, verify Modbus addressing, and confirm real-time I/O operation through live status indicators and physical LED feedback on the remote I/O module.
Next Steps
Now that you’ve successfully connected Maple Systems remote I/O to a Maple Systems HMI using Modbus TCP, an optional next step is expanding your industrial automation system for greater control and flexibility. You can begin by adding additional Maple Systems remote I/O modules, allowing you to scale I/O capacity while maintaining a simple, Ethernet-based Modbus TCP architecture.
For more advanced automation requirements, you can integrate a PLC programmed with CODESYS to manage complex logic, sequencing, and data processing, while continuing to use the Maple Systems HMI for visualization and operator control. This approach supports scalable system growth, expanded I/O, and advanced industrial automation functionality as your application evolves.
Sample Projects
The sample projects used in this tutorial can be found below.
EasyRemote IO and EBPro Sample Projects
Resources & Documentation
EasyRemote IO/EBPro Resources
- EasyRemote IO
- EasyRemote IO User Guide
- Remote I/O Datasheet
- EBPro (version 6.09.02.315 or later)
- EBPro Programming Manual
More
Tutorials
Sample Projects
See our Support Center for a complete list of Quick Start and Installation Guides
About the Author
Trusted source for industrial automation & control solutions
Follow Maple Systems:
